Multiband WSPR transceiver
Interesting links
Some interesting links on the Weak Signal Propagation Reporter (WSPR) protocol:
Short description
This project implements a standalone multiband WSPR transceiver with all the WSPR signal processing done by Red Pitaya in the following way:
- simultaneously record WPSR signals from eight bands
- use FPGA for all the conversions needed to produce .c2 files (complex 32-bit floating-point data at 375 samples per second)
- use on-board CPU to process the .c2 files with the WSPR decoder
- upload decoded data to wsprnet.org
With this configuration, it is enough to connect Red Pitaya to an antenna and to a network. After switching Red Pitaya on, it will automatically start operating as a WSPR receiver.
The transmitter part is disabled by default and should be enabled manually.
Hardware
The FPGA configuration consists of eight identical digital down-converters (DDC). Their structure is shown in the following diagram:
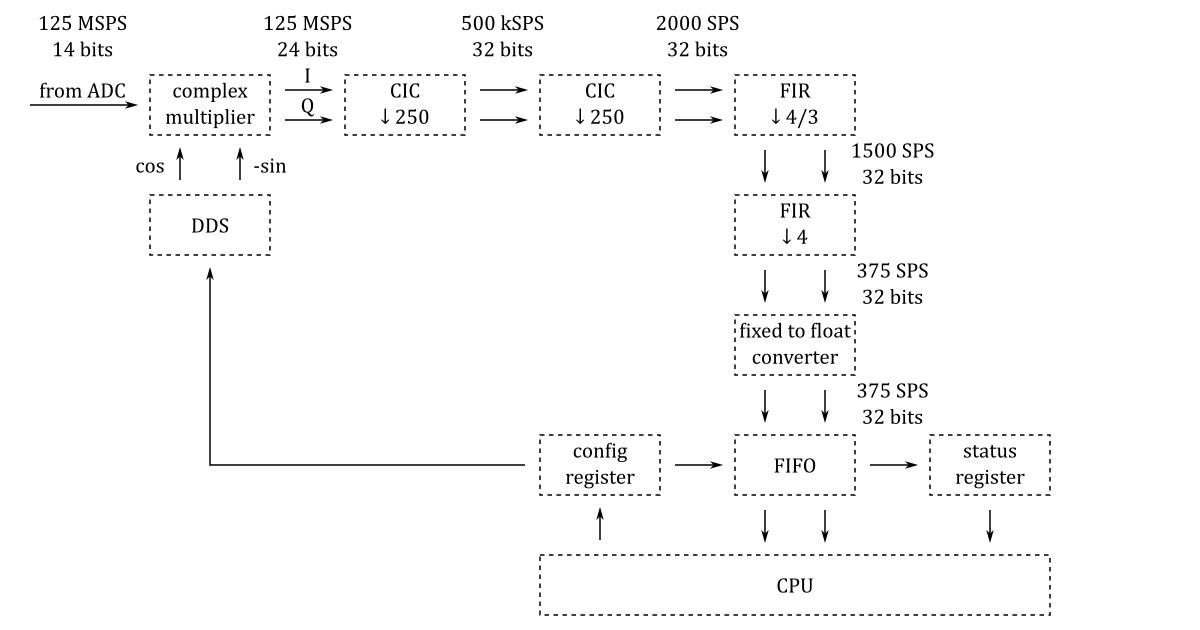
The DDC output contains complex 32-bit floating-point data at 375 samples per second and is directly compatible with the WSPR decoder.
The projects/sdr_transceiver_wspr directory contains three Tcl files: block_design.tcl, rx.tcl and tx.tcl. The code in these files instantiates, configures and interconnects all the needed IP cores.
Software
The write-c2-files.c program accumulates 42000 samples at 375 samples per second for each of the eight bands and saves the samples to eight .c2 files.
The recorded .c2 files are processed with the WSPR decoder.
The decoded data are uploaded to wsprnet.org using curl.
The decode-wspr.sh script launches write-c2-files, wsprd and curl one after another. This script is run every two minutes by the following cron entry in wspr.cron:
1-59/2 * * * * cd /dev/shm && /media/mmcblk0p1/apps/sdr_transceiver_wspr/decode-wspr.sh >> decode-wspr.log 2>&1 &The transmit-wspr-message.c program transmits WSPR messages.
GPS interface
A GPS module can be used for the time synchronization and for the automatic measurement and correction of the frequency deviation.
The PPS signal should be connected to the pin DIO3_N of the extension connector E1. The UART interface should be connected to the UART pins of the extension connector E2.
The measurement and correction of the frequency deviation is disabled by default and should be enabled by uncommenting the following line in wspr.cron:
1-59/2 * * * * cd /dev/shm && /media/mmcblk0p1/apps/common_tools/update-corr.sh 125 >> update-corr.log 2>&1 &Getting started
- Download SD card image zip file (more details about the SD card image can be found at this link).
- Copy the contents of the SD card image zip file to a micro SD card.
- Optionally, to start the application automatically at boot time, copy its
start.shfile fromapps/sdr_transceiver_wsprto the topmost directory on the SD card. - Install the micro SD card in the Red Pitaya board and connect the power.
Configuring WSPR receiver
By default, the uploads to wsprnet.org are disabled and all the decoded data are accumulated in /dev/shm/ALL_WSPR.TXT.
All the configuration files and scripts can be found in the apps/sdr_transceiver_wspr directory on the SD card.
To enable uploads, the CALL and GRID variables should be specified in decode-wspr.sh. These variables should be set to the call sign of the receiving station and its 6-character Maidenhead grid locator.
The frequency correction ppm value can be adjusted by editing the corr parameter in write-c2-files.cfg.
The bands list in write-c2-files.cfg contains all the WSPR frequencies. They can be enabled or disabled by uncommenting or by commenting the corresponding lines.
Configuring WSPR transmitter
The WSPR message, transmit frequency and frequency ppm value can be adjusted by editing transmit-wspr-message.cfg.
Building from source
The installation of the development machine is described at this link.
The structure of the source code and of the development chain is described at this link.
Setting up the Vitis and Vivado environment:
source /opt/Xilinx/2025.2/Vitis/settings64.shCloning the source code repository:
git clone https://github.com/pavel-demin/red-pitaya-notes
cd red-pitaya-notesBuilding sdr_transceiver_wspr.bit:
make NAME=sdr_transceiver_wspr bitBuilding SD card image zip file:
source helpers/build-all.shFeedback and results
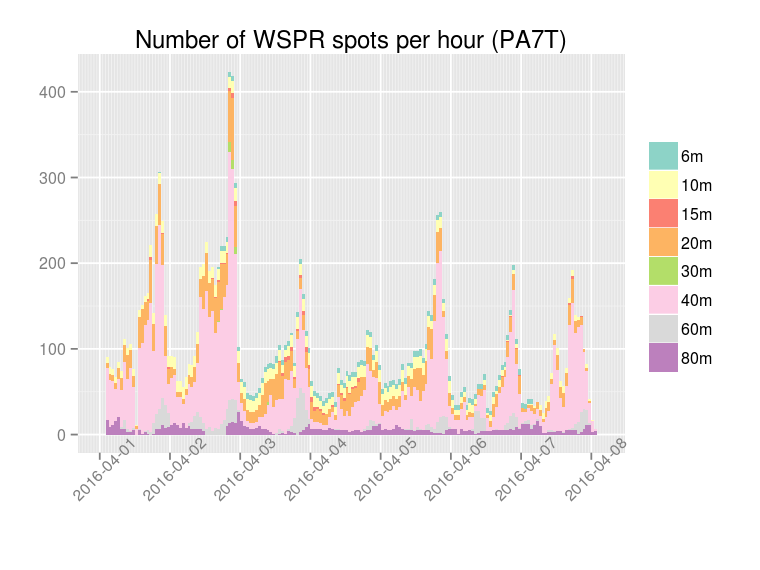
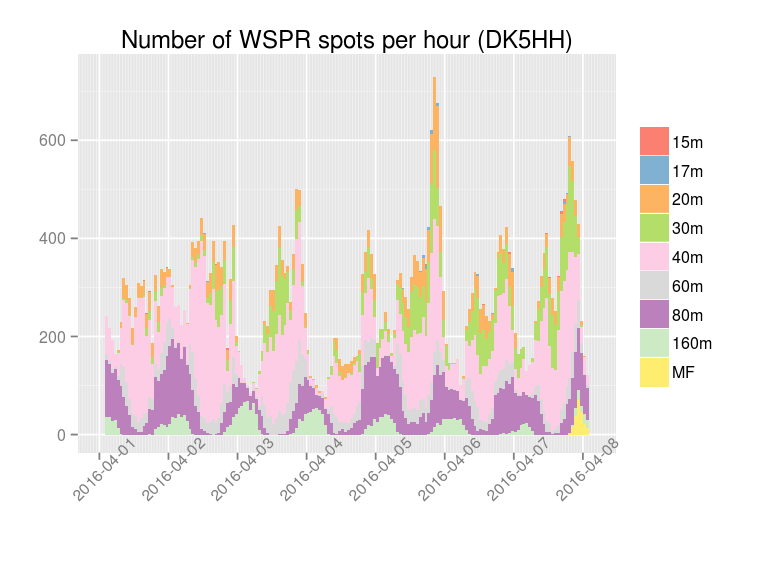
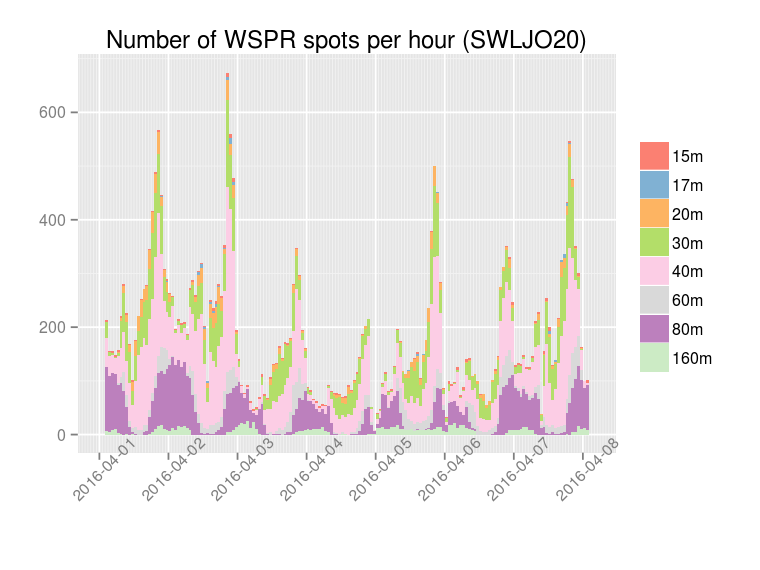
I would like to thank PA7T and DK5HH for their interest in this project, for the tests that they have done and for the valuable feedback that they have provided.
The following plots show the number of WSPR spots per hour decoded by the multiband WSPR receiver: